According to Allianz Risk Barometer, 45% of experts consider cyber incidents to be the most dreaded cause of business losses, surpassing both natural disasters and energy concerns.“We are in a time where data is currency, a single act of vandalism can bring any enterprise to its knees,” says Jason Harlam, Business Development Manager at Technology Advisory Group.
Downtime, damaged reputations, and plummeting customer trust can turn even the most prepared business leader’s nightmares into reality. No one expects to find digital graffiti scrawled across their corporate website or see valuable data sabotaged overnight, but it happens far more often than you’d think.
Are you prepared to handle this invisible menace lurking in the background? Let’s pull back the curtain and reveal precisely how cyber vandals operate and, more importantly, how you can stay one step ahead.
Secure Your Systems with TAG’s Proven Cybersecurity SolutionsTake proactive steps to protect your business with our expert security strategies. |
What is Cyber Vandalism?
It describes the unauthorized alteration, defacement, or sabotage of digital platforms, typically to spread a message, create chaos, or gain attention. Unlike espionage-focused cybercrimes, vandalism often aims to damage or humiliate rather than steal data.
According to GeekforGeeks, these acts can include graffiti-like defacement of your website or targeted attacks designed to cripple your operations. The damage hits your bottom line in two ways:
- Financial Loss: Extra costs for remediation, website restoration, and potential legal fees. According to CloudSecureTech, 60% of small companies that get hit by a cyber attack go out of business within six months.
- Reputational Damage: Customers lose faith in your online presence, and negative press can linger.
Not Just a Hacker’s Playground
Cyber vandalism differs from hacking for profit; it often stems from a desire for notoriety or vengeance. However, the repercussions can be equally devastating, including operational shutdowns, shunning by customers, and expensive repairs.
Common Tactics Cyber Vandals Use
Cyber vandals employ a diverse range of disruptive methods, from website defacement to insider sabotage.
Understanding these tactics is your first step to staying one move ahead and protecting your digital presence. When you know what to look for, you can proactively strengthen your defenses and limit the damage these threats can cause.
1. Website Defacement
Website defacement is one of the most visible forms of digital vandalism. Attackers might replace your homepage content with their own images, statements, or “tags” to make a public spectacle. Often, it’s not just about financial gain—cyber vandals may have political or ideological motivations, or they might simply be seeking online notoriety.
How It Happens:
- Exploiting known vulnerabilities in content management systems (CMS) or server software.
- Guessing or stealing admin credentials through phishing or brute-force attempts.
- Injecting rogue scripts via unsecured plugins or outdated software.
Key Precautions:
- Keep your CMS and all plugins regularly updated.
- Implement strong password policies and two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Monitor site logs and error reports to detect unusual activity early.
2. Digital Graffiti & Malware Injections
Digital graffiti involves inserting offensive text, images, or links that disrupt the appearance and functionality of your site. Malware injections take this a step further by embedding malicious code into your system or web pages, potentially capturing customer data or spreading viruses to users who visit your site.
How It Happens:
- Leveraging insecure code or missing patches in your website framework.
- Embedding malicious scripts (e.g., JavaScript, SQL injections) through form fields or weak validation processes.
- Overwriting legitimate data or files with corrupted versions that carry a hidden payload.
Real Consequences:
- Redirecting your traffic to scam sites, causing reputational damage.
- Stealing confidential data or planting ransomware to lock you out of your own systems.
- Disrupting site functionality, leading to lost sales and diminished user trust.
Early Detection Tips:
- Conduct regular security scans and integrity checks.
- Use automated scanning tools that can flag unfamiliar code snippets.
- Review Microsoft’s official security documentation for detailed steps on spotting malicious code and fixing vulnerabilities.
3. DDoS Attacks
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack involves flooding your network or servers with massive amounts of automated traffic, overloading your systems until legitimate users can’t access your services. Unlike data-focused attacks, the goal is often pure disruption—taking your website or infrastructure offline for as long as possible.
How It Works:
- Attackers use botnets (networks of compromised computers) to generate huge traffic spikes.
- Thousands or even millions of these “zombie” machines send requests simultaneously.
- Your servers crash or slow to a crawl under pressure, resulting in service outages and frustration for clients.
Preventative Measures:
- Deploy DDoS protection services and configure content delivery networks (CDNs) to absorb malicious traffic.
- Use rate limiting and traffic filtering rules to identify and block suspicious IP addresses.
- Establish a clear DDoS response plan that includes immediate steps to reroute traffic and protect critical services.
4. Insider Threats
Not all vandalism originates from outside the company. Sometimes, disgruntled employees, former contractors, or partners with privileged access can sabotage systems from within. Insider threats are particularly dangerous because these individuals already know your infrastructure and its weak points.
Potential Motivations:
- Personal grievances, such as perceived unfair treatment or workplace conflict.
- Financial incentives, like selling proprietary information to competitors or criminals.
- Ideological reasons, where an employee disagrees strongly with business decisions or ethics.
Risk Minimization:
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) so only necessary personnel have permission to critical systems.
- Conduct rigorous offboarding processes, revoking access rights as soon as an employee leaves.
- Monitor internal activity for anomalies, such as large data exports or unusual login times, and address suspicious behavior promptly.
Red Flags that Signal a Potential Attack
Early recognition can be the difference between a small hiccup and a full-blown crisis. Keeping an eye out for unexplained slowdowns, unusual traffic surges, or unexpected modifications to your website is key. Once you spot these signs, rapid intervention can prevent a cascade of damage.
1. Unexplained System Slowdowns
A sudden drop in website or network performance is often a red flag. Malicious scripts, hidden DDoS attempts, or even crypto-mining malware can rapidly consume system resources and affect everything from page load times to server responsiveness.
What to Watch For
- Spikes in CPU or memory usage without any clear cause.
- Frequent timeouts or error pages, even during off-peak hours.
- Server logs showing an unusual number of requests in a short timespan.
Proactive Measures
- Use performance monitoring tools that track real-time resource usage.
- Schedule automated stress tests to gauge system limits under heavy loads.
- Implement server-level rate limiting so one user (or bot) doesn’t hog capacity.
2. Suspicious IP Activities
Repeated failed login attempts, login attempts from unfamiliar regions, or drastic increases in traffic at odd hours can signal malicious intent. Analytics platforms can help identify these anomalies; for instance, Google Analytics provides detailed geographical data, while server logs reveal patterns or repeated requests from the same IP addresses.
What to Watch For
- Multiple login failures in quick succession—indicative of brute-force attempts.
- Sudden international traffic spikes when your business primarily serves local customers.
- IP addresses hitting sensitive areas of your site, like admin pages, excessively.
Proactive Measures
- Set up IP-based blocks or CAPTCHAs after a certain number of failed logins.
- Configure alerts to notify you if specific IPs trigger repeated login attempts.
- Conduct regular IP reputation checks and block known malicious sources.
3. Content Alterations
Changes to your site’s visuals or text that you didn’t authorize—such as odd images, offensive language, or unexplained links—are often direct indicators of sabotage. Even subtle adjustments, like small text modifications in critical pages, can undermine user trust and hint at a deeper system compromise.
What to Watch For
- Unexpected pop-ups, redirect links, or embedded ads that violate brand guidelines.
- Distorted images or replaced company logos.
- Altered text on landing pages, product listings, or FAQ sections.
Proactive Measures
- Automate file integrity monitoring to quickly flag unauthorized edits.
- Maintain version control of web files, so you can restore the original content.
- Train your team to promptly report any site irregularities, no matter how minor.
4. Actionable Tips for Early Detection
Monitor Logins
Stay vigilant with admin and server logs. Regularly review who accessed your systems and when. If you spot activity outside normal working hours or repeated login errors, investigate immediately.
Set Alerts
Configure your systems to generate alerts for anomalies such as unusual traffic, file edits in sensitive directories, or large data transfers. According to best practices from industry groups like the SANS Institute, timely alerts can drastically reduce the impact of cyber threats.
Quarantine When in Doubt
Segment compromised servers or user accounts to contain the damage. Network segmentation prevents an attacker from moving laterally across your environment. If possible, use a dedicated incident response process so everyone knows how to isolate threats quickly.
| More articles you might like: |
Practical Strategies to Protect Your Business
Proactive security measures can turn the tide against malicious actors. While no single solution guarantees invulnerability, combining multiple strategies can significantly reduce your risk and enhance overall resilience.
1. Harden Your Perimeter
A strong perimeter is the first hurdle cyber vandals must overcome. Firewalls, software patches, and secure server configurations work in tandem to block attempts before they reach your core systems.
Why It Matters
- Cybercriminals frequently look for outdated software with known vulnerabilities.
- Insecure server setups can leave open ports or default credentials that attackers exploit.
- Firewalls and intrusion prevention systems filter out harmful traffic, safeguarding your network boundaries.
How to Implement
- Regularly apply updates to operating systems, applications, and devices.
- Conduct vulnerability scans to identify misconfigured servers or software loopholes.
- Follow guidelines from the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on routine patching and best practices for locking down servers.
2. Employee Cyber Training
Your employees serve as both the first and last line of defense. Without proper training, they may unintentionally open phishing emails or click on suspicious links, allowing attackers easy entry.
Why It Matters
- A single click on a malicious link can install malware or reveal credentials.
- Social engineering attacks target human trust, bypassing even the most advanced technical safeguards.
- Ongoing awareness programs keep threats top-of-mind, building a culture of vigilance.
How to Implement
- Host regular workshops or webinars on recognizing phishing attempts.
- Create simulated phishing campaigns to test staff readiness.
- Encourage employees to report suspicious activity immediately and reinforce that no question is too small.
3. Backup & Recovery Protocols
Conducting routine backups of mission-critical data is essential. If vandals succeed in defacing or encrypting your systems, backups let you restore normal operations with minimal downtime.
Why It Matters
- Having multiple data copies across different locations ensures a “safety net” if primary files are compromised.
- Off-site or cloud-based backups protect you from localized disasters, such as natural events or physical theft.
- Versioning allows you to roll back to a clean state even if recent files get corrupted.
How to Implement
- Schedule automated backups, verifying they include all important data.
- Store at least one backup set offline or in a secure cloud environment.
- Test your recovery process regularly to confirm backups can be restored quickly when needed.
4. Intrusion Detection & Monitoring
Modern security tools, or the services of a Managed Service Provider (MSP), can detect red flags—like unauthorized login attempts or unusual traffic—around the clock, helping you contain incidents faster.
Why It Matters
- Early detection limits damage to minutes or hours rather than days or weeks.
- Continuous monitoring uncovers anomalies you might miss, such as data exfiltration attempts or malicious code injections.
- Rapid response can help isolate issues before they spread to multiple systems or user accounts.
How to Implement
- Deploy intrusion detection or prevention systems (IDS/IPS) for real-time alerts.
- Monitor event logs using a centralized dashboard so abnormal activity stands out.
- Consider partnering with an MSP if you lack in-house security expertise.
5. Vendor Vetting & Access Management
Third-party vendors and software providers can inadvertently expose your network if their security standards fall short. Limiting their access to only the systems or data they need reduces potential damage if they’re compromised.
Why It Matters
- A breach via a trusted vendor could grant attackers a direct path into your network.
- Some vendors might skip crucial updates or rely on outdated security protocols.
- By segmenting and monitoring vendor access, you minimize the scope of potential vulnerabilities.
How to Implement
- Conduct thorough due diligence on each new vendor’s security policies.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) so external partners only see relevant systems.
- Create clear guidelines for password policies, patching schedules, and escalation procedures.
6. Incident Response Plan
Preparation is a game-changer when cyber vandals strike. A robust incident response plan outlines exactly what to do, who to involve, and how to communicate both internally and externally.
Why It Matters
- Swift, coordinated action limits damage and downtime.
- Designated roles prevent confusion about who handles containment, recovery, or public statements.
- Regular drills keep staff practiced and alert, so real incidents prompt immediate, effective action.
How to Implement
- Document clear, step-by-step procedures for various attack scenarios.
- Assign roles: Who coordinates the technical response, who informs leadership, and who communicates with customers.
- Hold tabletop exercises or simulations at least annually, refining your plan based on lessons learned.
7. Legal & Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance doesn’t eliminate reputational fallout, but it can offset financial burdens like legal fees, forensic investigations, and compliance penalties. Legal counsel helps you navigate complex regulations and liabilities when incidents do occur.
Why It Matters
- Certain industries have strict compliance obligations (e.g., healthcare, finance).
- A legal expert ensures you fulfill breach notification requirements and avoid lawsuits.
- Insurance policies can cover data restoration costs or pay for public relations efforts if customer trust falters.
How to Implement
- Consult a legal professional to clarify your compliance obligations and draft incident-reporting protocols.
- Identify an insurance plan tailored to your industry’s risk level, covering both data breaches and vandalism.
- Periodically review policies and coverage limits to keep pace with evolving threats and business needs.
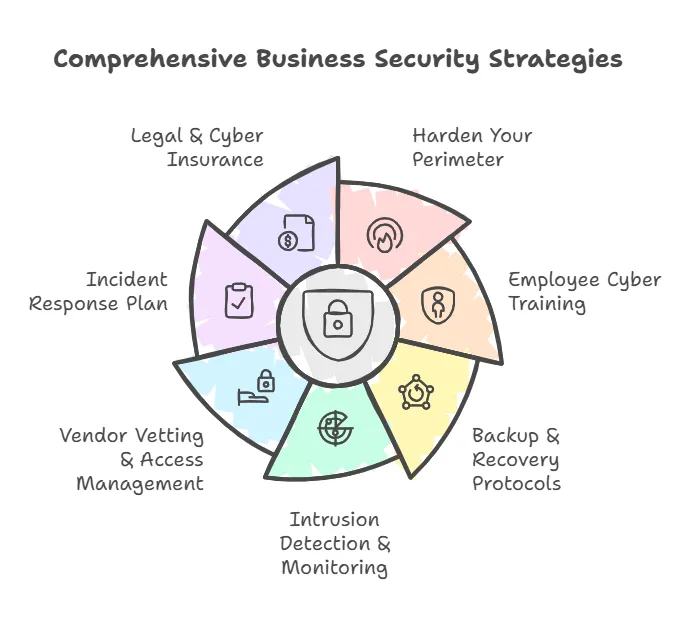
Bringing It All Together
Each of these strategies—hardened perimeters, comprehensive training, robust backup procedures, continuous monitoring, careful vendor management, an ironclad incident response plan, and proper legal/insurance frameworks—forms part of a holistic defense against cyber vandalism.
Implementing even a few of these measures can substantially lower your risk and help ensure business continuity, no matter what threats come your way.
Practical Steps to Counter Cyber Vandalism
| Protective Measure | Description | Benefit |
| Multi-Layered Security | Use firewalls, antivirus, IDS/IPS | Blocks various attack vectors |
| Regular Employee Training | Educate staff about threats & safe practices | Reduces risk of human error |
| Access Control & Encryption | Grant permissions sparingly & encode sensitive data | Minimizes unauthorized data access |
| Backups (Online & Offline) | Maintain data copies on secure, separate servers | Enables quick recovery without ransom payment |
| Ongoing Monitoring & Audits | Track network activity for unusual patterns | Early detection of unauthorized changes |
Take the Next Step with Technology Advisory Group
Businesses that invest in strong cybersecurity stand a far better chance of avoiding catastrophic downtime or loss of trust. Cyber vandalism is a growing threat, and awareness alone won’t cut it—you need proactive measures, airtight policies, and consistent monitoring. Whether the perpetrator is a rogue hacker a thousand miles away or a disgruntled insider, data destruction can strike when least expected.
Technology Advisory Group is ready to help you stay ahead of cybersecurity. Don’t wait until you’re dealing with digital graffiti on your website or scrambled customer data. Reach out to Technology Advisory Group for more information and to schedule a consultation.
| Discover Trusted Cybersecurity Services Near You:
|
Schedule Your Cloud Services Consultation
Ready to make a move to the cloud? TAG is ready to help with any or all cloud services from a private cloud, public cloud, or Microsoft 365 services.



