Data breaches and cyber-attacks are more common than ever. Many businesses underestimate the importance of a robust network security plan until it’s too late.
As Jason Harlam, Business Development Manager at Technology Advisory Group, says, “Implementing a network security plan not only protects your business but also builds trust with clients and partners who rely on your commitment to data security”.
A single security breach can compromise sensitive information, disrupt operations, and damage a company’s reputation, and your risk of becoming a target is higher than ever. 2023 had the highest number of cyber attacks on record, beating 2021’s previous record by 72%.
To avoid these risks, businesses must proactively protect their digital assets. This blog will guide you through the essential elements of building a comprehensive network security plan.
Understanding the Basics of Network Security
Network security involves implementing measures to protect data and resources’ integrity, confidentiality, and availability. It encompasses various strategies and technologies designed to safeguard your network infrastructure from cyber threats. The key components of a successful network security implementation include:
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These tools act as the first line of defense, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that it cannot be read without the decryption key even if it is intercepted.
- Access Control: Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized users can access specific network resources, reducing the risk of insider threats.
Stop Worrying About Cyber Attacks Crippling Your Network!Ensure robust protection with TAG’s advanced network security solutions. |
The Importance of a Network Security Plan
A network security plan outlines the policies, procedures, and technologies necessary to protect network infrastructure from unauthorized access and other security risks. It’s a comprehensive approach to ensure your data’s integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
This plan serves as a blueprint for implementing network security measures that safeguard against cyber threats and mitigate potential damages from security breaches.
Steps to Building a Network Security Plan
1. Assess Your Current Security Posture
Begin by evaluating your existing network security measures. Identify vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of your current defenses. This assessment should include:
- Network Mapping: Create a detailed map of your network infrastructure, including all devices, connections, and data flows.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Use automated tools to scan for known vulnerabilities and weak points in your network.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the potential impact of different types of security breaches on your business operations.
2. Define Security Policies and Procedures
Clear, comprehensive security policies and procedures are the foundation of any effective network security plan. These should cover:
- Password Policies: Enforce strong password practices, including regular updates and complex passwords.
- User Access Controls: Define who has access to what information and under what circumstances. Limit access rights using the principle of least privilege.
- Data Handling Procedures: Establish guidelines for handling sensitive information, including data encryption and secure data disposal methods.
3. Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments. This strategy limits the spread of cyber attacks and makes it easier to manage and secure different parts of your network. Implementing network segmentation can include:
- Creating VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks): Separate different departments or types of data traffic to minimize the impact of a security breach.
- Using Firewalls Between Segments: Deploy internal firewalls to monitor and control traffic between segments, adding an extra layer of protection.
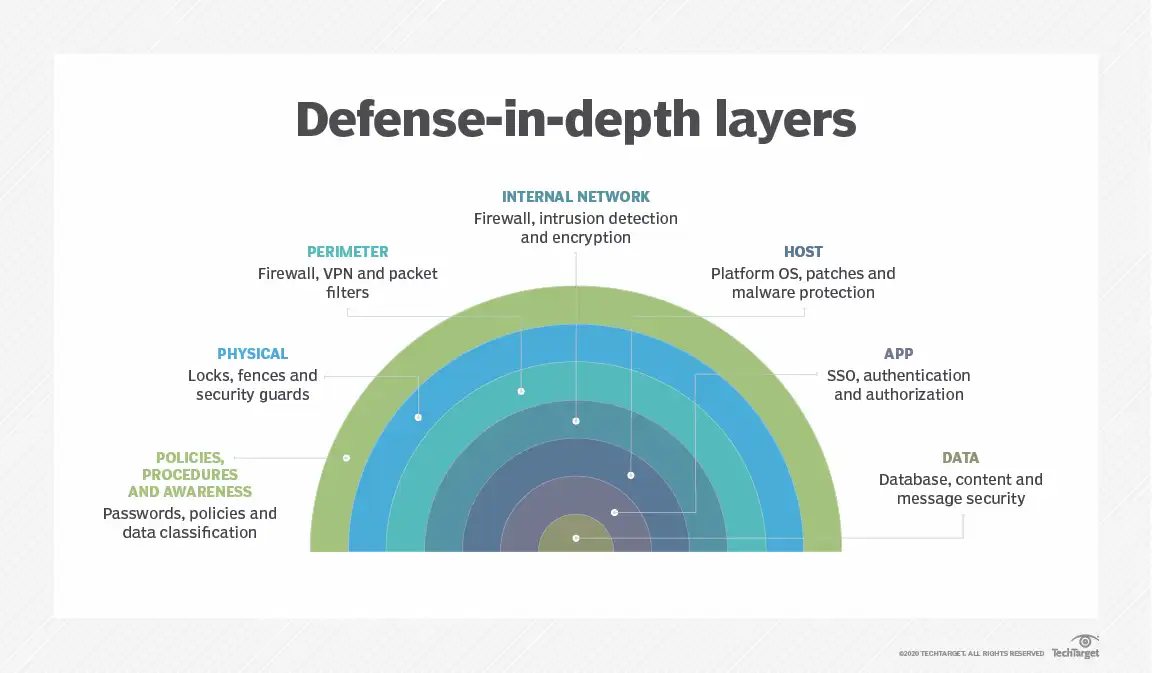
Source: TechTarget
4. Develop an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines the steps your organization will take in the event of a security breach. It should include:
- Detection and Analysis: Procedures for identifying and assessing the scope of a security incident.
- Containment and Eradication: These are steps to contain the breach, minimize damage, and remove the threat from your network.
- Recovery and Post-Incident Analysis: Guidelines for restoring normal operations and analyzing the incident to prevent future breaches.
Common Network Security Threats and Mitigation Strategies
| Threat | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
| Phishing Attacks | Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication. | Employee training, email filtering, multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Malware | Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. | Antivirus software, regular updates, and employee training. |
| Ransomware | A type of malware that encrypts the victim’s data, demanding a ransom to restore access. | Regular backups, endpoint security, and email filtering. |
| Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks | Intercepting and altering communication between two parties without their knowledge. | Encryption, secure network protocols, VPNs. |
| Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) | Overwhelming a network or website with traffic to make it unavailable to users. | DDoS protection services, network traffic monitoring, and rate limiting. |
| Insider Threats | Security breaches caused by individuals within the organization, intentionally or unintentionally. | Strict access controls, employee monitoring, and regular audits. |
| SQL Injection | Inserting malicious SQL queries into input fields to manipulate or access the database. | Input validation, using parameterized queries, and regular security testing. |
| Zero-Day Exploits | Attacks that target previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware. | Regular updates, patch management, and threat intelligence services. |
| Weak Passwords | Easily guessable or reused passwords that can be exploited by attackers. | Enforce strong password policies, MFA, and regular password changes. |
| Unpatched Software | Software that has not been updated with the latest security patches, leaving it vulnerable to exploits. | Regular patch management, automated updates, and vulnerability scanning. |
5. Employee Training and Awareness
Employees are often the weakest link in network security. Regular training and awareness programs are crucial to ensuring that all staff members understand their role in protecting the network. Focus on:
- Phishing Awareness: 74% of account takeover attacks start with phishing. Educate employees about common phishing tactics and how to recognize suspicious emails.
- Security Best Practices: Teach staff about strong password policies, safe internet usage, and the importance of reporting suspicious activity.
- Regular Training Sessions: Conduct regular training sessions to keep employees updated on the latest security threats and best practices.
6. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping your systems and software up to date is essential for protecting against security vulnerabilities. Implement a schedule for:
- Regular Updates: Ensure all software, including operating systems and applications, are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
- Vulnerability Management: Continuously monitor for new vulnerabilities and apply patches as soon as they become available.
- Automated Updates: Where possible, enable automated updates to reduce the risk of human error.
7. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to access network resources. This can include:
- Something You Know: A password or PIN.
- Something You Have: A smartphone or security token.
- Something You Are: Biometric verification, such as a fingerprint or facial recognition.
| More resources you might like: |
Implementing Network Security: Best Practices
✅Develop a Clear Implementation Plan: Outline the steps required to implement network security measures. This plan should include timelines, responsible parties, and specific tasks.
✅Involve Stakeholders: Engage all relevant stakeholders, including IT staff, management, and employees, in the implementation process. Collaboration ensures that everyone understands their role in maintaining network security.
✅Test and Validate: Before fully deploying security measures, test them in a controlled environment to ensure they work as intended. Then, validate their effectiveness through regular testing and monitoring.
✅Continuous Improvement: Network security is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your security measures to address new threats and vulnerabilities.
Achieve Robust Network Security with Technology Advisory Group
A well-crafted network security plan is indispensable in safeguarding your business against cyber threats. By prioritizing network security implementation and staying vigilant against evolving risks, you can fortify your organization’s defenses and protect sensitive data.
| Discover Trusted Network Support Services Near You
|
Protecting your business from cyber threats requires a proactive approach. For expert guidance on building a robust network security plan, consider partnering with a trusted cybersecurity advisor such as Technology Advisory Group, we specialize in safeguarding businesses through comprehensive security solutions.
Contact us today to schedule a free consultation and strengthen your defenses against cyber threats.
Schedule Your Cloud Services Consultation
Ready to make a move to the cloud? TAG is ready to help with any or all cloud services from a private cloud, public cloud, or Microsoft 365 services.


